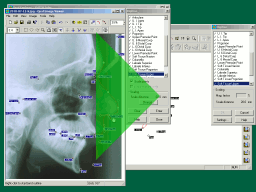
OPAL can save x-ray tracings as SVG files that can be edited using
Inkscape. In Inkscape you can modify line thicknesses, change fonts,
remove unwanted parts of the tracing, add captions, combine with other
images - the list is endless. Inkscape can then export modified tracings
as bitmap images which can be imported into Powerpoint, etc.
 Inkscape is an Open Source vector
graphics editor, with capabilities similar to Illustrator, CorelDraw,
or Xara X, using the W3C standard Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) file
format.
Inkscape is an Open Source vector
graphics editor, with capabilities similar to Illustrator, CorelDraw,
or Xara X, using the W3C standard Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) file
format.
The outline editing using Bezier curves first introduced in OPAL 2.3
is designed to work in a similar way to the curve editing provided by
Inkscape - so once you are comfortable with curve editing in either
program, you will probably find it easy to edit curves in the other.